If you’re experiencing joint pain and stiffness in your foot and ankle you may require the expertise of an arthritis and rheumatism specialist or a podiatrist who specializes in arthritis of the feet. These specialists are pivotal in diagnosing and treating conditions that impact foot and ankle health, including common culprits like osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), as well as other related ailments such as gout, which can present similar symptoms. As we dive into the nuances of OA and RA, understanding their unique characteristics is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Osteoarthritis: The Wear and Tear Arthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA), often referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis, is the most prevalent form of arthritis and is one of several common types of foot arthritis. OA primarily affects the cartilage – the protective tissue at the ends of bones. Over time, factors like aging, obesity, or previous injuries contribute to the gradual erosion of the cartilage around joints.
The joints in the foot and ankle are weight-bearing, meaning they are particularly susceptible to this type of arthritis. Common osteoarthritis symptoms include pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility. While OA of the foot and ankle is a localized condition, it can significantly affect your mobility and overall quality of life.
In addition to its common symptoms, arthritis specialists often emphasize the importance of recognizing early signs, such as subtle changes in gait and occasional discomfort. Early intervention can make a substantial difference in managing osteoarthritis effectively. Holistic treatment plans may involve a combination of pain management strategies, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications tailored to your needs.
Rheumatoid Arthritis in Feet: Symptoms and Management
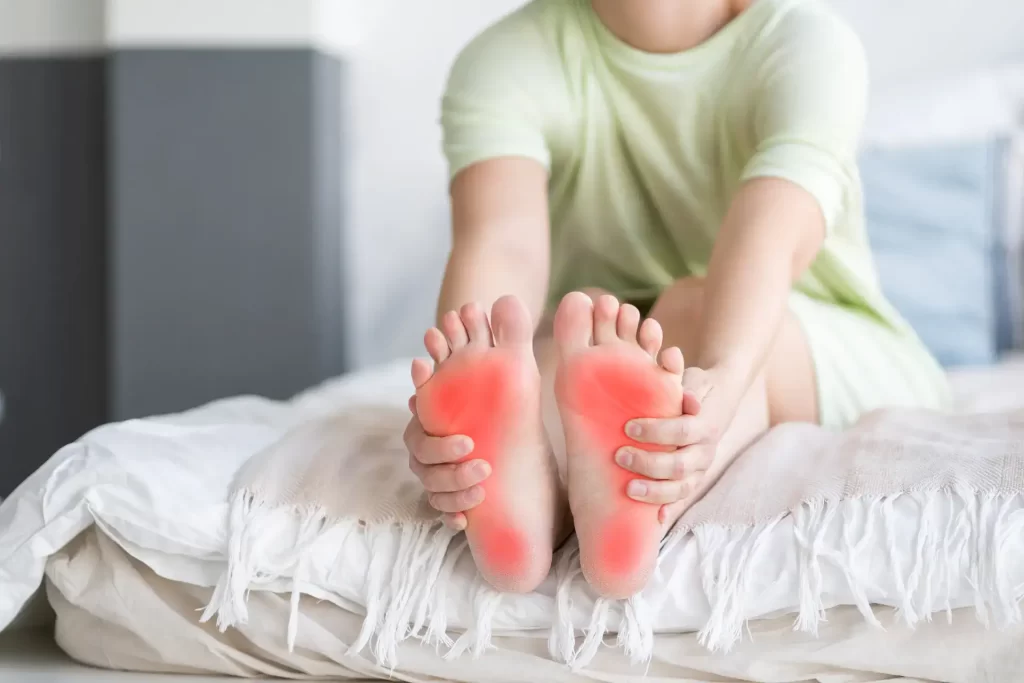

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the body’s joints, causing inflammation. When RA targets the lower extremities, it can result in arthritic feet and ankle arthritis, presenting early symptoms such as pain, swelling, and stiffness that typically affect both sides of the body equally.
Along with these symptoms, rheumatoid arthritis nodules and rashes could also appear, which require diagnosis and treatment by a specialist for effective management. Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis in feet may entail a strategic combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, and potentially surgery to manage the discomfort and maintain mobility.
Tackling the full impact of RA on the foot and ankle requires a comprehensive approach to care. Specialists who treat RA create personalized treatment plans that include a mix of traditional treatment options – such as NSAIDs and corticosteroids – and cutting-edge treatments like biologics and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These newer treatments offer the potential for better symptom management and can help in slowing the progression of joint damage, thereby enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
What is the Difference Between Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Differentiating between osteoarthritis – the “wear and tear” condition that typically affects cartilage in high-stress joints like knees and hips asymmetrically – and rheumatoid arthritis – the autoimmune disease that causes symmetrical joint inflammation and systemic symptoms such as fatigue and loss of appetite – is fundamental for effective treatment.
Diagnostic methods play a critical role in differentiating the two types of arthritis: X-rays reveal the cartilage loss indicative of osteoarthritis, while MRI scans and specific blood tests for RF and anti-CCP antibodies are used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis. These unique signs guide the development of tailored treatments, ranging from physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments for osteoarthritis to more advanced therapies like DMARDs and biologics for rheumatoid arthritis.
Accurate diagnosis is key to choosing the most appropriate and individualized approach for these conditions, ensuring better outcomes for patients. Lifestyle changes and physical therapy can significantly benefit those with osteoarthritis, whereas rheumatoid arthritis may demand a bolder treatment strategy to mitigate joint damage and systemic symptoms. Such personalized care strategies are essential for improving joint health and overall quality of life, underlining the importance of distinct treatment responses for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Surgery: When is it considered?
When conservative treatments like medication fail to sufficiently manage rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in the feet and ankles, and severe joint damage leads to substantial pain, disability, or deformity, various types of rheumatoid arthritis surgery may be considered as a next step. This intervention, aimed at relieving pain, improving function, and enhancing quality of life, becomes a viable path for patients when other methods prove inadequate.
Surgical options – including synovectomies, tendon repairs, joint fusion, and total joint replacement – are determined based on the extent of RA’s impact. A synovectomy to remove inflamed tissue may be enough, or more involved procedures such as arthrodesis or arthroplasty may be required to restore joint stability and mobility.
Following surgery, a carefully planned rehabilitation process is essential to ensure a full recovery. Post-surgical physical therapy is often prescribed to rebuild strength and mobility. This postoperative care is a crucial element of the treatment plan, alongside ongoing medications and lifestyle modifications, to maintain overall joint health and mitigate the chance of future damage.
Alternative Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Beyond conventional treatments, individuals may explore alternative approaches to rheumatoid arthritis treatment. These alternative options can include dietary changes, complementary therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Dietary modifications, such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, have shown potential in reducing inflammation and improving overall well-being. Additionally, practices like acupuncture, mindfulness-based stress reduction, and therapeutic exercises complement traditional treatments, contributing to a more holistic and patient-centered approach.
Complementary and alternative therapies are gaining prominence in rheumatoid arthritis management and many arthritis and rheumatism specialists recognize the value of incorporating these approaches into comprehensive care plans. Engaging in open discussions with arthritis and rheumatism specialists is important for making informed decisions about integrating these alternatives into your overall treatment plan.
While medication and surgery remain standard treatments, complementary approaches may enhance the overall management of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.Navigating the complexities of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis is key to the effective management of these conditions, and it often requires a collaborative approach with skilled arthritis and rheumatism specialists. These healthcare professionals are essential in providing guidance, managing symptoms, and crafting individualized treatment plans.